















Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.), an important source of vegetable oil, nutraceuticals, functional foods, and housing materials, provides raw materials for a repertoire of industries engaged in the manufacture of cosmetics, soaps, detergents, paints, varnishes, and emulsifiers, among other products. The palm plays a vital role in maintaining and promoting the sustainability of farming systems of the fragile ecosystems of islands and coastal regions of the tropics. In this study, we present the genome of a dwarf coconut variety ‘‘Chowghat Green Dwarf’’ (CGD) from India, possessing enhanced resistance to root (wilt) disease. Utilizing short reads from the Illumina HiSeq 4000 platform and long reads from the Pacific Biosciences RSII platform, we have assembled the draft genome assembly of 1.93 Gb.
The genome is distributed over 26,855 scaffolds, with *81.56% of the assembled genome present in scaffolds of lengths longer than 50 kb. About 77.29% of the genome was composed of transposable elements and repeats. Gene prediction yielded 57,660 Transcripts. A total of 112 nucleotide-binding and leucine-rich repeat loci, belonging to six classes, were detected. We have also undertaken the assembly and annotation of the CGD chloroplast and mitochondrial genomes. The availability of the dwarf coconut genome shall prove invaluable for deducing the origin of dwarf coconut cultivars, dissection of genes controlling plant habit and fruit color, and accelerated breeding for improved agronomic traits.
*Keywords: Cocos nucifera, dwarf cultivar, disease resistance, de novo assembly, organellar genomes, agri-genomics, nutrigenomics
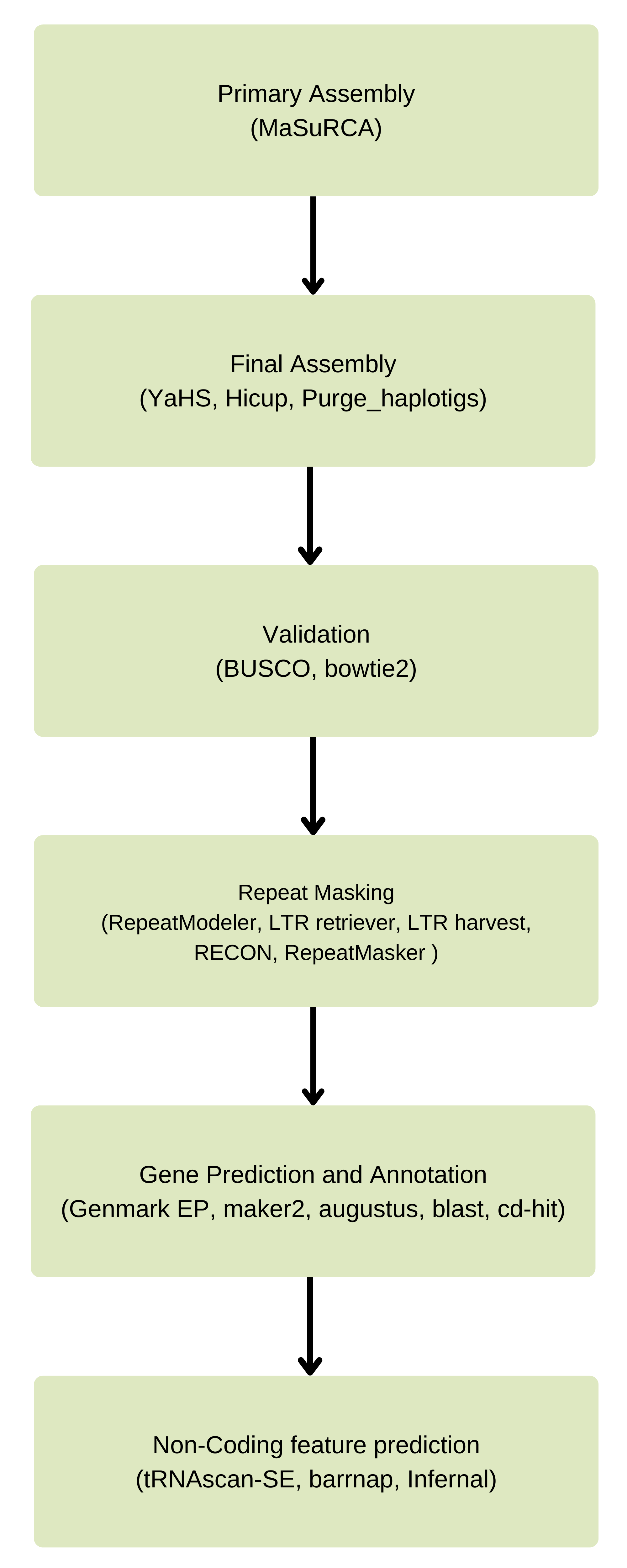
Primary Assembly:
Final Assembly:
Validation
Tool used - BUSCO(v5.4.7)
The final assembly was assessed for genome completeness with BUSCO using its single copy
orthologue
database for embryophyta_odb10.
Tool used - bowtie2(v2.4.1)
The raw WGS illumina short reads were aligned to the genome to assess the percentage of
reads
mapping to the genome.
Repeat Masking:
Gene Prediction and Annotation:
Non-coding feature prediction:
Comparison of Final Assembly Statistics of the Genome of Chowghat Green Dwarf Variety Using Two Assemblers
| Assembly features | Masurca |
|---|---|
| Total no of contigs | 1930 |
| Total no of bases(bp) | 2,688,203,608(~2.7 Gb) |
| Min contig length(bp) | 1013 |
| Max contig length(bp) | 241,587,684(~241.6 Mb) |
| Average contig length(bp) | 1,392,851(~1.4Mb) |
| N50 contig size(bp) | 174,886,800(~174.8 Mb) |
| (G+C)% | 37.70% |
| #N’s | 0.12% |
*MaSuRCA, Maryland Super Read Cabog Assembler.